What Is Ethereum? The Only Guide You Actually Need

It runs the code behind almost everything in crypto.
You have heard the name. You have seen it on every exchange, every headline, every portfolio tracker. Ethereum is the second largest cryptocurrency in the world. But most people still cannot explain what it actually does.
Here is the problem. Every "What is Ethereum" article buries you in jargon. Smart contracts. Gas fees. Proof of Stake. Solidity. By the third paragraph, you are more confused than when you started.
This guide fixes that. It breaks Ethereum down to its core, explains every moving part in plain language, and uses current data from February 2026 to show you exactly where the network stands today.
No fluff. No filler. Just answers.
What Is Ethereum in Simple Terms?
Ethereum is a global, open source blockchain platform where developers build applications that run without any central authority. Think of it as a world computer. Instead of running software on servers owned by Google or Amazon, Ethereum runs software across thousands of machines worldwide at the same time.
The network launched on July 30, 2015. It was created by Vitalik Buterin, who was 19 at the time, along with cofounders Gavin Wood, Charles Hoskinson, Anthony Di Iorio, and others.
Bitcoin lets you send and receive digital money. That is its job. Ethereum lets you send money AND build entire applications on top of it. Lending platforms. Trading exchanges. Digital art marketplaces. Insurance systems. All running automatically through code.
Key stats as of February 2026:
How Does Ethereum Work?
Ethereum works by executing programs called smart contracts on a decentralized network of computers, with every transaction verified and recorded on a public blockchain. No single company runs the show. Thousands of nodes around the world do.
Three components make the system function:
The Blockchain stores every transaction and every smart contract interaction since launch. It is public. Anyone can read it. Nobody can change it.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the engine. When a developer deploys a smart contract, the EVM ensures the code runs exactly as written. Same inputs, same outputs, every single time. No interference. No override.
Ether (ETH) is the fuel. Every action on Ethereum costs a small fee called gas, paid in ETH. Gas compensates the people who maintain and secure the network. When the network is busy, gas fees rise. When it is quiet, fees fall.
Since the EIP 1559 upgrade, a portion of every gas fee is permanently burned. This means some ETH is destroyed with each transaction. During periods of high activity, more ETH gets burned than gets created. This makes ETH potentially deflationary.
What Are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a self executing program stored on the Ethereum blockchain that automatically enforces the terms of an agreement when specific conditions are met. No lawyer. No bank. No middleman. The code is the contract.
Here is the simplest analogy. A vending machine. You insert money. You press a button. The machine delivers the product. No negotiation. No trust required. The machine follows the rules every time.
Smart contracts work the same way, except they handle financial agreements worth billions. A lending protocol uses a smart contract to match borrowers and lenders. A decentralized exchange uses one to set token prices automatically. An NFT marketplace uses one to transfer ownership and payment in a single transaction.
Developers write smart contracts in a language called Solidity, which is similar to JavaScript. Once deployed, the contract lives at a permanent address on Ethereum. Anyone can interact with it. Anyone can read the code before they do.
The catch: bugs in smart contracts can be exploited. Unlike regular software, you cannot just push a quick patch. This is why security audits from firms like OpenZeppelin and Trail of Bits exist. They are essential, but they are not a guarantee.
What Is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake (PoS) is the consensus mechanism Ethereum uses to validate transactions and secure the network, where participants lock up ETH as collateral instead of competing with mining hardware.
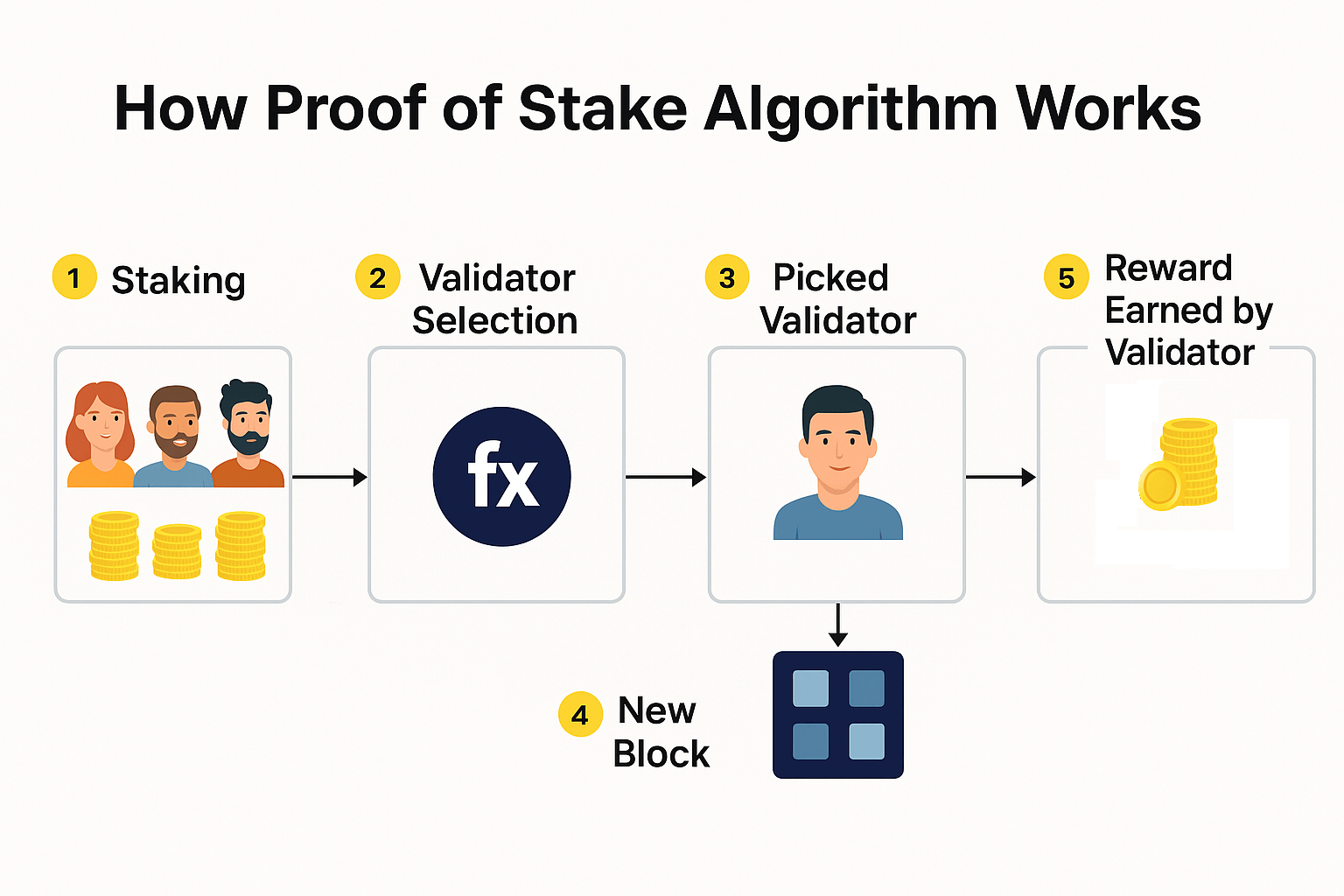
Before September 15, 2022, Ethereum used Proof of Work, the same system Bitcoin still uses. Miners competed to solve puzzles. The winner got to add the next block. It worked, but it consumed as much electricity as a mid sized country.
The Merge changed everything. Ethereum switched to Proof of Stake in what became the most significant technical upgrade in blockchain history. Energy consumption dropped by 99.95% overnight.
Under the new system, validators stake a minimum of 32 ETH (roughly $64,000 at current prices) as collateral. The network randomly selects validators to propose and confirm new blocks. Honest validators earn rewards. Dishonest validators get slashed, meaning a portion of their staked ETH is destroyed.
As of early 2026, approximately 30% of the total ETH supply (about 36.8 million ETH) is staked. This creates significant locked supply that cannot be freely sold, which some analysts view as structurally bullish for the price.
For those who cannot afford 32 ETH, liquid staking solves the problem. Protocols like Lido let you stake any amount. You deposit ETH and receive a liquid token called stETH in return. That stETH can be traded, used as collateral in DeFi, or lent out, all while your original ETH earns staking rewards. Lido holds approximately $27.5 billion in total value locked, making it the single largest protocol in all of DeFi.
What Is ETH Used For?
ETH serves as transaction fuel, staking collateral, DeFi base currency, and a store of value within the Ethereum ecosystem.

Transaction fees (gas). Every interaction with Ethereum costs gas, paid in ETH. Sending tokens. Swapping on a decentralized exchange. Minting an NFT. Deploying a smart contract. All require ETH.
Staking. Validators lock ETH to secure the network and earn approximately 3% to 5% annually in rewards.
DeFi collateral. ETH is the backbone of decentralized finance. It is used as collateral for loans on Aave and MakerDAO, as liquidity in Uniswap pools, and as the primary trading pair across hundreds of protocols.
NFT purchases. The vast majority of NFT transactions happen in ETH. From digital art on OpenSea to gaming items and virtual real estate.
Store of value. With EIP 1559 burning a portion of supply and staking locking up 30%, some investors view ETH as a productive asset that generates yield while becoming scarcer over time.
Ethereum vs Bitcoin: What Is the Difference?
Bitcoin is designed to be digital money. Ethereum is designed to be a programmable platform. Both are valuable. They serve different purposes.
Supply. Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million coins. Ethereum has no fixed cap, but the burn mechanism means net supply can decrease when the network is busy enough.
Speed. Bitcoin produces a block roughly every 10 minutes. Ethereum produces one every 12 seconds.
Programmability. Bitcoin has limited scripting. Ethereum can run complex applications, entire financial systems, games, social networks, and governance tools.
Consensus. Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (mining). Ethereum uses Proof of Stake (staking).
Energy. Bitcoin mining consumes roughly 150 TWh per year. Ethereum's Proof of Stake uses a tiny fraction of that.
Most serious investors hold both. Bitcoin is the reserve asset. Ethereum is the application layer. They complement each other more than they compete.
Ethereum vs Solana: Which Is Better?

Ethereum prioritizes security and decentralization, then scales through Layer 2 networks. Solana prioritizes speed on a single chain. Neither approach is objectively superior. Each involves tradeoffs.
Solana processes 2,000 to 4,000 transactions per second at fractions of a penny per transaction. Ethereum's base layer handles 15 to 30 TPS, though Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum and Base offer comparable speed and cost.
On DeFi depth, Ethereum dominates. Ethereum and its Layer 2 ecosystem hold over $100 billion in total value locked. Solana holds approximately $8 to $10 billion.
On raw transaction volume, Solana leads. The network processes over 2.3 billion transactions per month, more than any other chain.
Ethereum has the longer track record, the larger developer community, and deeper institutional adoption. Solana has the speed, the user experience, and the momentum. Many builders and investors are active in both ecosystems.
What Is Layer 2 and Why Does It Matter?
Layer 2 networks are separate blockchains built on top of Ethereum that process transactions faster and cheaper while inheriting Ethereum's security.

Ethereum's base layer is slow and expensive by design. That is the tradeoff for maximum decentralization and security. Layer 2 solutions fix the user experience without sacrificing those properties.
Rollups are the dominant technology. They process hundreds or thousands of transactions off chain, compress the data, and post a summary back to Ethereum for final verification. Users get fast, cheap transactions. Ethereum gets the fees and the security role.
Major Layer 2 networks include:
- Arbitrum: The largest by TVL. Popular for DeFi.
- Optimism: Powers the OP Stack framework. Base is built on it.
- Base: Developed by Coinbase. Growing rapidly.
- zkSync: Uses zero knowledge proofs for cryptographic verification.
The Dencun upgrade in March 2024 introduced blob storage (EIP 4844), a new data type specifically for Layer 2 rollups. It cut Layer 2 posting costs by up to 90%.
As of early 2026, Ethereum Layer 2 networks collectively hold over $43 billion in total value locked. That number is growing faster than the base layer itself.
What Is DeFi on Ethereum?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) is a system of financial applications on Ethereum that replaces banks and brokers with smart contracts. Lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest all happen through code.
Ethereum hosts approximately 68% of all DeFi value locked across the blockchain industry. The numbers are massive:
- Lido: ~$27.5 billion TVL (liquid staking)
- Aave: ~$27 billion TVL (lending and borrowing)
- EigenLayer: ~$13 billion TVL (restaking)
- Uniswap: ~$6.8 billion TVL (decentralized exchange)
- MakerDAO: ~$5.2 billion TVL (stablecoin issuance)
The total DeFi market saw a decline from $120 billion to $105 billion in early February 2026 as crypto markets pulled back. But the drop was driven by falling asset prices, not user exits. The amount of ETH deployed in DeFi actually increased during this period, rising from 22.6 million to 25.3 million ETH. Users stayed put and kept farming yield.
A Short History of Ethereum
Ethereum has survived hacks, bear markets, a complete consensus overhaul, and the collapse of its biggest ecosystem partners. It keeps running.

2013: Vitalik Buterin publishes the Ethereum whitepaper at age 19.
2014: The Ethereum Foundation raises ~31,000 BTC ($18 million) in a public crowdsale.
2015: Ethereum launches on July 30 with the Genesis Block.
2016: The DAO hack drains $60 million in ETH. The community hard forks the chain to reverse the theft, splitting into Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC).
2017 to 2018: The ICO boom. Thousands of projects raise billions by issuing ERC 20 tokens. Many are scams. The SEC cracks down.
2020: DeFi Summer. Protocols like Compound and Uniswap ignite a wave of yield farming. TVL explodes from under $1 billion to over $10 billion in months.
2021: NFT mania. Beeple sells a digital artwork for $69 million at Christie's. Ethereum TVL peaks near $180 billion.
2022: The reckoning. Terra/Luna collapses in May, wiping $40 billion. Celsius, Three Arrows Capital, and FTX fall in sequence. In September, The Merge transitions Ethereum to Proof of Stake.
2024: Spot Ethereum ETFs launch in the United States. The Dencun upgrade slashes Layer 2 costs.
2025: ETH hits a new all time high of $4,951 in August. Institutional adoption accelerates through ETFs and corporate treasury strategies. The Fusaka upgrade activates in December.
2026: ETH trades near $2,000 after a market correction. The Glamsterdam upgrade is scheduled for the first half of the year. 30 day active addresses reach 14.74 million, a decade high.
What Are the Risks of Investing in Ethereum?
Ethereum carries significant risks including price volatility, smart contract exploits, regulatory uncertainty, competition from rival chains, and centralization pressure in staking.
Price volatility is extreme. ETH hit $4,951 in August 2025 and trades near $2,000 five months later. That is a roughly 60% decline.
Smart contract risk has cost the industry billions. Bugs in code lead to exploits. The composability of DeFi means one failure can cascade across connected protocols.
Regulatory uncertainty lingers. Spot Ethereum ETFs are trading in the US, which implies regulatory acceptance. But ETF outflows remain a concern. One recent day in February 2026 saw $113.1 million in net outflows from Ethereum spot ETFs.
Competition from Solana, Avalanche, and other Layer 1 blockchains threatens market share. Layer 2 solutions help Ethereum compete on cost and speed, but they also fragment liquidity and complicate the user experience.
Staking centralization is a valid concern. Lido alone controls a substantial portion of staked ETH. If too much stake concentrates in a few entities, the decentralization promise erodes.
How to Buy ETH in 2026
You can buy ETH on any major cryptocurrency exchange in minutes. The process is straightforward.
Step 1: Create an account on an exchange. Bitunix, Kraken, and Bybit are the most commonly used.
Step 2: Complete identity verification (KYC). This typically requires a government ID and a selfie.
Step 3: Deposit funds. Bank transfer, debit card, credit card, or stablecoin transfer.
Step 4: Place a buy order for ETH. Use a market order for instant execution or a limit order to set your preferred price.
Step 5: Transfer to a self custody wallet for long term storage. Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor offer the strongest security. Software wallets like MetaMask and Phantom provide convenience and direct access to DeFi.
The golden rule: if your ETH is sitting on an exchange, you do not fully control it. The exchange holds the keys. Move significant holdings to your own wallet.
Is Ethereum a Good Investment?
Ethereum's investment case rests on its position as the dominant smart contract platform, growing institutional adoption, and a supply dynamic that trends toward scarcity.
Standard Chartered projects ETH could reach $7,500 by end of 2026. Citi targets $4,300 to $5,400. More conservative analysts expect ETH to trade in the $2,800 to $4,800 range this year.
The bull case: 30% of supply is staked. EIP 1559 burns ETH with every transaction. Spot ETFs provide institutional access. Layer 2 adoption is accelerating. The Fusaka and Glamsterdam upgrades improve scalability.
The bear case: ETH is down 60% from its August 2025 high. Layer 2 networks capture fees that used to go to the base layer. Solana is eating market share in consumer applications. Macro headwinds from high interest rates limit risk appetite.
This article does not recommend buying or selling ETH. It provides the information you need to make your own decision. Always do your own research. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.
The Bottom Line
Ethereum is the infrastructure layer of the decentralized internet. It powers lending protocols that manage $27 billion in deposits. It runs exchanges that process billions in daily volume. It hosts stablecoins that serve as the base currency of an entire parallel financial system.
Is it perfect? No. Gas fees spike. Hacks happen. The price can drop 60% in five months.
But a decade after launch, with 14.74 million active addresses, over $100 billion locked across its ecosystem, and every major financial institution building products around it, Ethereum is no longer an experiment.
It is infrastructure. And the builders are not done.
This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry significant risk. Always conduct your own research before making any investment decisions.




