What Is Bitcoin? The Complete Guide for 2026

Bitcoin is the first and largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. Launched in January 2009, it introduced a way to send value across the internet without relying on banks, payment processors, or any central authority. Sixteen years later, BTC remains the most widely recognized digital asset on the planet, with a market cap that has at times exceeded $2 trillion.
But what exactly is Bitcoin, how does it work, and why should you care? This guide breaks it all down.
Bitcoin in Simple Terms
Bitcoin is digital money. Unlike the dollar or the euro, no government prints it, no central bank controls its supply, and no single company runs its network. Instead, Bitcoin operates on a peer to peer system where transactions are verified by thousands of computers spread across the globe.
Think of it this way: when you send money through a bank, that bank acts as the middleman. It confirms you have the funds, deducts the amount from your account, and credits it to the recipient. Bitcoin removes that middleman entirely. The network itself handles verification through a process called mining, and every transaction is recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain.
How Bitcoin Works?
Three core components power the Bitcoin network:
The Blockchain is a public, tamper resistant record of every Bitcoin transaction ever made. Each "block" contains a batch of transactions, and once verified, it gets chained to the previous block. This creates an unbreakable timeline that anyone can audit but no one can alter.
Mining is the process by which new transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain. Miners use specialized hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle earns the right to add the next block and receives newly minted BTC as a reward. This is how new bitcoins enter circulation.
Private and Public Keys serve as your digital identity on the network. Your public key is like your email address, and anyone can send you BTC with it. Your private key is like your password, and whoever holds it controls the funds. Lose your private key and your Bitcoin is gone forever. There is no customer support hotline to call.
Why Does Bitcoin Have Value?
Bitcoin derives its value from several properties that make it unique among both traditional currencies and digital assets:
Fixed Supply. Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist. This hard cap is written into the protocol and cannot be changed. As of 2026, roughly 19.8 million BTC have already been mined. This built in scarcity is often compared to gold, which is why Bitcoin earned the nickname "digital gold."
Decentralization. No single entity controls Bitcoin. The network is maintained by tens of thousands of nodes across every continent. Shutting it down would require simultaneously disabling every node, which is practically impossible.
Censorship Resistance. No government or institution can freeze your Bitcoin or prevent you from sending it. This property makes BTC particularly valuable in countries with unstable currencies or authoritarian financial controls.
Portability. You can carry a billion dollars worth of Bitcoin in your head by memorizing a 12 word seed phrase. Try doing that with gold bars.
The Halving: Bitcoin's Built In Monetary Policy
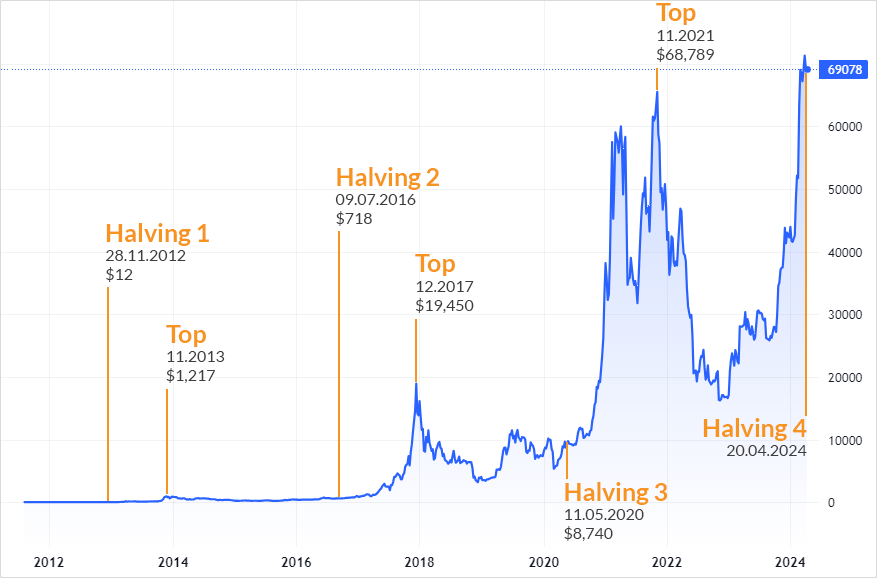
Every 210,000 blocks (roughly every four years), the mining reward gets cut in half. This event is called the "halving." When Bitcoin launched in 2009, miners earned 50 BTC per block. After the most recent halving in April 2024, that reward dropped to 3.125 BTC.
This deflationary mechanism ensures that the supply of new Bitcoin entering the market decreases over time. Historically, halvings have preceded significant price increases, though past performance never guarantees future results.
Bitcoin Price History: A Brief Timeline
Bitcoin has experienced extraordinary volatility since its inception:
In 2010, a programmer paid 10,000 BTC for two pizzas. At current prices, those pizzas would be worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
In 2017, BTC surged from around $1,000 to nearly $20,000 before crashing more than 80% the following year.
In 2021, Bitcoin hit $69,000 before entering another prolonged downturn.
In October 2025, BTC reached a new all time high above $126,000, fueled by institutional adoption and the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States.
As of February 2026, Bitcoin trades in the $65,000 to $70,000 range after a steep correction from its October peak.
How to Buy Bitcoin?
Purchasing Bitcoin in 2026 is straightforward. The most common methods include:
Centralized Exchanges such as Coinbase, Bitunix, Binance, and Kraken allow you to buy BTC with a bank transfer or credit card. These platforms handle custody for you, meaning they hold your private keys.
Self Custody Wallets like Ledger, Trezor, or software wallets such as Sparrow give you full control over your private keys. This is the approach serious holders prefer because it eliminates counterparty risk.
Bitcoin ETFs allow you to gain exposure to BTC through traditional brokerage accounts. Spot Bitcoin ETFs launched in the U.S. in January 2024 and attracted billions of dollars in inflows, though recent months have seen significant outflows.
Risks and Criticisms
No honest guide would skip the risks:
Volatility. Bitcoin can drop 20% or more in a single week. It has happened multiple times throughout its history and will likely happen again.
Regulatory Uncertainty. Governments worldwide continue to develop frameworks for cryptocurrency. Regulations can significantly impact adoption and price.
Environmental Concerns. Bitcoin mining consumes substantial energy. While a growing share of mining uses renewable sources, the energy debate persists.
Security Risks. Not from the network itself, which has never been hacked, but from user error. Lost keys, phishing attacks, and exchange hacks remain real threats.
Is Bitcoin Money?
This depends on who you ask. Bitcoin meets several of the criteria economists use to define money: it is divisible (down to eight decimal places called satoshis), durable (it exists as long as the network runs), portable, and scarce. Where it falls short, for now, is as a widely accepted medium of exchange. Most people hold BTC as an investment rather than spending it on daily purchases.
Whether Bitcoin eventually becomes a global reserve asset, remains a niche investment, or fades into obscurity is one of the most consequential financial questions of our era. What is clear is that after sixteen years, the network keeps running, blocks keep being mined, and the conversation around decentralized money is not slowing down.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your own research before making investment decisions.




